How Do Hearing Aids Work?
Book a Free Hearing Aid Trial


We Served 2,00,000+ Customer Across India
Hearing aid machines are complex electronic devices that are designed to amplify sound and improve the hearing ability of individuals suffering from hearing loss.

Main Parts of a Hearing Aid
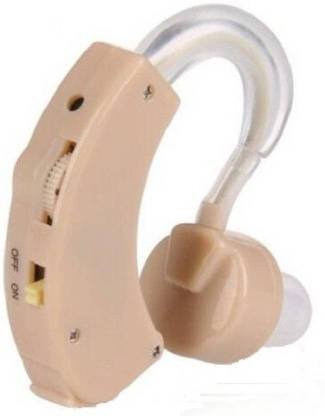
Ear Machines consist of several components, including a microphone, amplifier, digital signal processor (DSP), receiver/speaker, earpiece, control and adjustment, and battery. These components work together to capture, process, and amplify sound, making it more accessible and audible for individuals with hearing problems. The advancements in technology have led to the development of sophisticated hearing aid devices that offer improved sound quality, enhanced speech understanding, and customizable features for better hearing in various listening situations.
Here is a detailed explanation of how hearing aids work:

-
Microphone : The microphone is a crucial component of a hearing machine as it plays a fundamental role in capturing sound from the surrounding environment. It is typically located on the outer casing of the ear machine and is designed to pick up acoustic signals, including speech, music, and surrounding noise.
When sound waves enter the hearing aid device through the microphone, they interact with a diaphragm or membrane inside the microphone. This diaphragm is made of a material that is sensitive to changes in air pressure. When sound waves hit the diaphragm, they cause it to vibrate or move back and forth.
The movement of the diaphragm generates corresponding electrical signals. These signals represent the variations in air pressure caused by the sound waves. The microphone then converts these analog electrical signals into digital signals, which can be processed and amplified by the internal circuit of the hearing aid.
-
Digital Signal Processing (DSP): Digital signal processing (DSP) is a key technology used in modern digital hearing aid devices to enhance sound quality and provide individualized amplification. After the electrical signals from the microphone are amplified, they are processed by a digital signal processor.
The digital sound processing in hearing aids consists of a powerful microchip and specialized software that can perform complex calculations and analysis on the incoming signals in real time. The primary goal of DSP is to improve speech understanding and sound perception by manipulating and optimizing the amplified signals based on the individual's hearing needs and the listening environment.

-
Amplifier : The amplifier is a critical component in hearing aid machines that receives the electrical signals generated by the microphone. The primary function of an amplifier is to increase the strength or intensity of these signals, effectively amplifying them to a level that is suitable for the individual's hearing needs.
Once the electrical signals are received from the microphone, they are processed by the amplifier circuitry. The amplifier circuit consists of various electronic components, including transistors or integrated circuits, designed to boost the power of the signals without distorting their original characteristics.
The amplification process involves selectively increasing the volume of different frequency components of the signals. This is crucial because individuals with hearing loss may have difficulty hearing certain frequency ranges more than others. By amplifying specific frequency ranges, the hearing aid can compensate for the individual’s specific hearing loss profile.
-
Receiver/Speaker: Once the electrical signals have been processed and modified by the DSP, they are sent to the receiver. The receiver is a crucial component responsible for converting the electrical signals back into audible sound waves.
The receiver is typically housed within the hearing aid and is positioned near the ear canal. It consists of a miniature speaker or transducer that vibrates in response to the electrical signals it receives. These vibrations generate sound waves that travel through the ear canal and reach the eardrum.
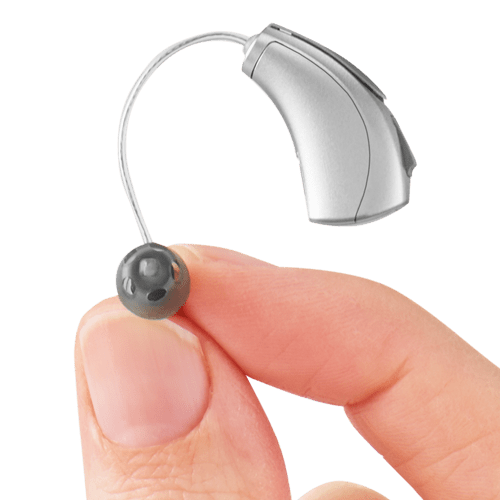

The receiver is designed to provide precise and accurate sound reproduction, ensuring that the modified signals are faithfully converted into audible sounds. It is carefully calibrated to meet the individual’s hearing needs, considering factors such as their hearing loss profile, desired amplification, and frequency response requirements.

-
Earpiece or Earmold: The earpiece or earmold is an important component of a hearing aid that helps direct the amplified sound waves into the ear canal. It ensures proper sound transmission from the ear machine to the eardrum, ultimately enhancing the individual's ability to hear.
The earpiece or earmold is designed to fit comfortably in the ear, providing a secure and comfortable fit. It can be custom-made to match the unique contours of the individual's ear, offering a personalised and precise fit. Alternatively, it may come in a generic size that can be adjusted or modified to achieve a better fit for the individual.
The material used for the earpiece is typically soft and flexible, such as silicone or acrylic, to ensure comfort during extended periods of wear.
- Battery: The battery is also a crucial component of a hearing aid as it provides the necessary electrical energy to power the device. Hearing aid batteries are typically located within the casing of the hearing aid device itself, making them easily accessible for replacement when needed. The size and type of battery used in a hearing aid depend on the specific model and design of the device.

Features of Hearing Aids
Modern digital hearing aids often include additional features to enhance the listening experience. These may include noise reduction algorithms to reduce background noise, control, and adjustment, feedback cancellation to eliminate whistling or feedback sounds, directional microphones to focus on sounds from specific directions, connectivity options for wireless streaming, and telecoil for compatibility with telephones and assistive listening devices.
- Noise Reduction: Hearing aids are equipped with advanced algorithms that help reduce background noise, allowing users to focus on speech and other important sounds.
- Feedback Cancellation: Feedback or whistling sounds can occur when sound leaks and gets re-amplified by the hearing aid. Feedback cancellation technology identifies and eliminates these sounds, providing a more pleasant and feedback-free listening experience.
- Directional Microphones: Many hearing machines feature directional microphones that can automatically or manually focus on sounds coming from specific directions.
- Connectivity Options: Wireless connectivity allows hearing aid devices to connect to various devices, such as smartphones, televisions, and audio streaming accessories.
- Telecoil (T-Coil): Telecoil technology enables compatibility with telephones, public address systems, and assistive listening devices that have a magnetic field, known as an induction loop. This feature allows users to directly receive sound signals from these systems, enhancing clarity and reducing background noise.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the parts of a hearing aid?
Hearing aids use these parts to help pick up and amplify sound from your environment and channel it into your ear: microphone, amplifier, speaker or receiver, battery, and earpiece.
What are the prices of digital hearing aids in India?
The digital hearing aids prices in India vary depending on the brand, model, and features, ranging from around INR 30,000 to several lakhs. Ear Logist can provide you with the best offers on digital hearing aids prices in India.
What is the price of programmable hearing aid in India?
The price of a programmable hearing aid in India depends on the specific model and features, ranging from around INR 25,000 to INR 1,00,000 or more.
How much do ear machines cost in India?
The cost of ear machines in India can vary widely depending on the type, brand, and features. It can range from as low as a few thousand rupees to several lakhs, depending on the sophistication and technology involved.
What are the 3 main components of a hearing aid?
Three components make up a hearing aid: a microphone, an amplifier, and a speaker. A microphone in the hearing aid picks up sound, transforms it into electrical impulses, and then transmits those signals to an amplifier. The signals are given more strength by the amplifier before being transmitted to the ear via a speaker.
Can hearing machines be controlled via smartphones?
Yes, most of the hearing machines can be controlled via smartphones using dedicated mobile apps. This allows users to adjust settings, and volume, and even stream audio directly to their hearing aids, enhancing their overall listening experience.
Where can I get the best hearing aids near me?
You can get the best hearing aids near you at Ear Logist, an authorized and trusted provider of top hearing aid brands. Ear Logist’ clinic/store/shop/center is available across India.